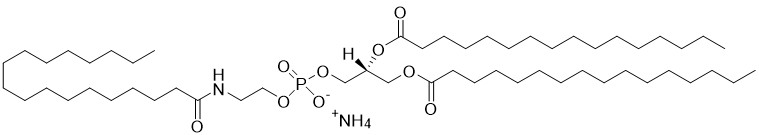
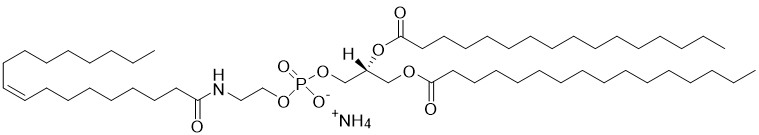
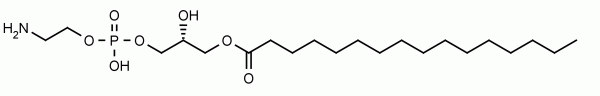
1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-stearoyl (N-stearoyl-DPPE) is a type of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) and an important intermediate in the endocannabinoid biosynthesis pathway. Fatty acid amides are formed by hydrolysis of NAPEs by a specific phospholiase D (NAPE-PLD), and metabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolases (FAAH). Both of these enzymes are emerging drug targets initially for the treatment of inflammatory pain and ischemia. Specifically, N-stearoyl-ethanolamine (SEA) is known for its in vivo anti-inflammatory properties including suppression of allergic dermatitis; and could be the mediator preventing obesity in C57BL/6J mice fed a high fat diet.
L-2418
N-Stearoyl-DPPE
1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-stearoyl (N-stearoyl-DPPE) is a type of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) and an important intermediate in the endocannabinoid biosynthesis pathway. [Read More...]