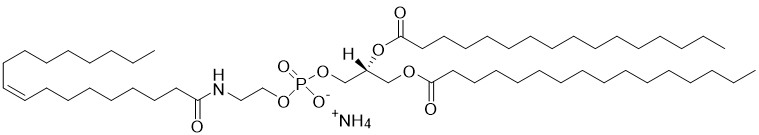
1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-oleoyl (N-oleoyl-DPPE) is a type of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) and an important intermediate in the endocannabinoid biosynthesis pathway. Fatty acid amides are synthesized by a specific phospholiase D (NAPE-PLD) and metabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolases (FAAH) and N-Acylethanolamine acid amidase (NAAA). These enzymes are drug targets for the treatment of inflammatory pain and nervous system disorders. N-oleoyl-ethanolamine (OEA) is particularly known for its anorexic effect producing satiety and reducing body weight gain in experimental animals on hypercaloric diets. Structural analogs of OEA and inhibitors of FAAH and NAAA are being explored as novel anti-obesity drugs. In addition, preclinical studies have shown that OEA is a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compound that exerts neuroprotective effects and the endogenous release of OEA could be a homeostatic signal to counteract the toxic actions of alcohol in both the periphery and CNS.
L-2419
N-Oleoyl-DPPE
1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-oleoyl (N-oleoyl-DPPE) is a type of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) and an important intermediate in the endocannabinoid biosynthesis pathway. [Read More...]