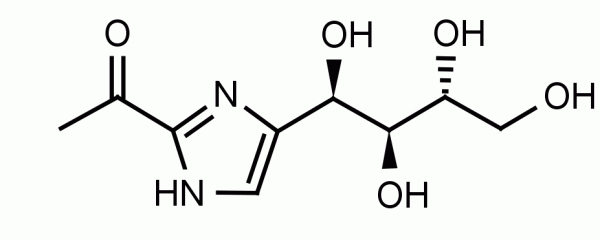
Isoprenoid compounds are a diverse group of natural products which are essential components in all cells. Isoprenoids are biosynthesized from the simple precursors isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). Eukaryotes, fungi, and some gram-positive bacteria produce IPP through the mevalonate (MVA) pathway whereas gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria utilize the non-mevalonate or 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway. MEP is formed from 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate (DXP) by MEP Synthase (DXP reductoisomerase) and coupled with CMP to form 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol (CDP-ME) by CDP-ME Synthase.
Provided as the sodium salt
Alternate Names: Methylerythritol phosphate, 2-C-Methylerythritol 4-phosphate, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate, Methylerythritol 4-phosphate
Bulk discounts available, please email echelon@echelon-inc.com for information.
Publications
1) Poliquin, K., Y. V. Ershov, et al. (2004). “Inactivation of sll1556 in Synechocystis Strain PCC 6803 Impairs Isoprenoid Biosynthesis from Pentose Phosphate Cycle Substrates In Vitro.” J Bacteriol 186(14): 4685-4693.
2) Eoh, H., A. C. Brown, et al. (2007). “Characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 4-Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-Methyl-d-Erythritol Synthase: Potential for Drug Development.” Journal of Bacteriology 189(24): 8922-8927.
3) Lherbet, C., F. Pojer, et al. (2006). “Absence of Substrate Channeling between Active Sites in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens IspDF and IspE Enzymes of the Methyl Erythritol Phosphate Pathway.” Biochemistry 45(11): 3548
4) Tsang, A., et al. (2011). “
5) Li, Z. and T. D. Sharkey (2012). “Metabolic Profiling of the Methylerythritol Phosphate Pathway Reveals the Source of Post-illumination Isoprene Burst from Leaves.” Plant, Cell & Environment 36(2): 429-437.
6) Price, K. E., et al. (2016). “Molecular Mechanism of Action of Antimalarial Benzoisothiazolones: Species-Selective Inhibitors of the Plasmodium spp. MEP Pathway enzyme, IspD.” Scientific Reports 6: 36777.

![Benzo[a]pyrene - Echelon Biosciences](https://www.echelon-inc.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/1452.gif)