Interest in ionizable lipids and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) continues to accelerate, and as the field grows novel cargos and lipid formulations are being explored to address common therapeutic barriers. mRNA-LNPs have proven successful, but the inherent disadvantages of mRNA such as short half-life and immunogenicity may prohibit its use in some therapeutic cases. To combat the issue of half-life, new types of RNA cargo are being developed such as self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) and circular RNA (circRNA). A less well-studied alternative cargo for LNPs is plasmid DNA.
Plasmid DNA (pDNA) has distinct advantages over RNAs in terms of stability, long term expression, and the ability to encode promoters that enable cell-specific expression. The chief drawback to using pDNA in vivo is that it is well known to activate the cGAS-STING pathway. cGAS is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates STING when bound to DNA and triggers an extensive cellular inflammatory response. Therefore, a secondary means of inhibiting inflammation must be included if pDNA is to be utilized in a LNP therapy. In the current study, Patel et al. provide evidence that inclusion of anti-inflammatory lipids in pDNA-LNP formulations blocks STING-mediated inflammation.
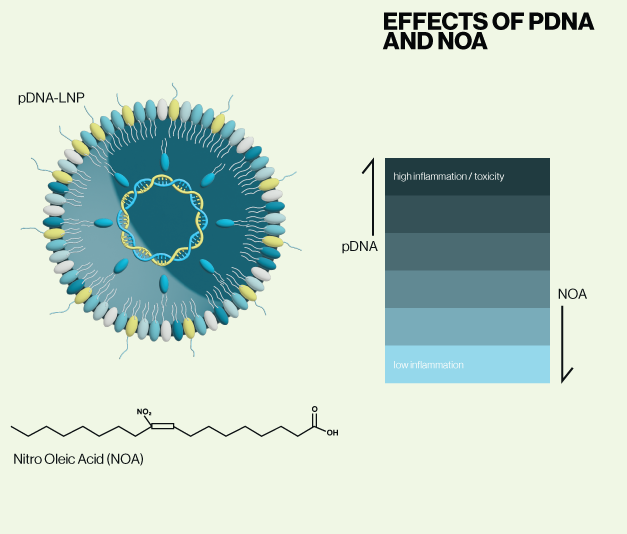
First, the authors establish that pDNA-LNPs activate cGAS-STING at similar levels to common transfection reagents in both cell culture and an animal model. These effects were also dose dependent. They next hypothesized that addition of specific unsaturated fatty acids such as Linoleic acid (LA), and Oleic acid (OA) could blunt the toxic effects of pDNA. These lipids have been shown to inhibit certain pro-inflammatory genes and activate antioxidant signaling pathways. Initial in vitro screens showed that nitrated versions of LA and OA (NLA, NOA - Echelon L-0112) dramatically reduced immune activation when added to pDNA-LNP formulations. Subsequent experiments provide evidence that pDNA toxicity is also abrogated in vivo when NOA is present in the LNP, and that reporter gene expression is sustained for several weeks.
Their current data suggest that NOA addition to LNPs could allow for pDNA to be used as a potential therapeutic cargo similar to siRNA and mRNA. Whether this strategy is generalizable to other types of nucleic acid LNPs was not explored, but it raises the possibility of anti-inflammatory components in LNPs in addition to or in place of nucleoside modified cargos.
Echelon's Ionizable lipids (D-Lin-MC3-DMA, ALC-0315, and SM-102), ALC-0159, and nitro-oleic acid (NOA) were used in this work (Cat# N-1282, N-1102, N-1020, L-0112, respectively).
Read the full article here:
Nature Biotechnology (2025)
0.2
/ 0.3
Related Articles
Stay informed with our informative blog posts.
0.3
/ 0.3
Get in Touch
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about our services, feel free to reach out to us. We’re here to help!
Biosciences