The Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) Assay Kit II is a sensitive, specific, and robust method for quantification of LPA in Plasma, Serum, and Tissue Homogenate.
Sample Types: Serum, Plasma, and Tissue homogenate (human or animal)
Sample Volume: 20 µL/sample (for duplicate points)
Assay Incubation Time: 2 hours and 30 minutes
Assay Range: 0.064 µM to 1,000 µM
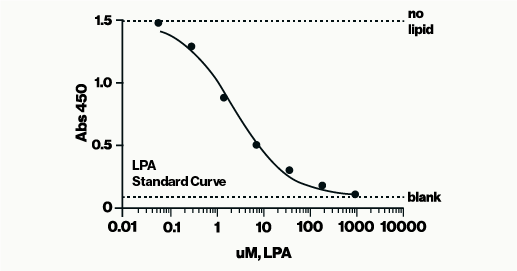
The LPA Assay is an ELISA designed for in vitro measurement of Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) in biological samples. This assay is specific for LPA and sensitive to different acyl chains.
How It Works
The LPA Assay follows a competitive ELISA format, where the colorimetric signal is inversely proportional to the amount of LPA present in the sample—higher LPA levels result in a weaker signal.
Assay Procedure
- Prepare Samples: Mix samples with a biotinylated anti-LPA antibody and sample diluent.
- Competitive Binding: Transfer mixtures to an LPA-coated detection plate.
- Detection: Add Streptavidin-HRP for binding and use colorimetric detection to measure biotinylated anti-LPA bound to the plate.
- Quantification: Determine LPA concentration using a standard curve with known amounts of LPA.
The assay is read at 450 nm and requires approximately 3 hours to complete.
Biological Significance of LPA
LPA is a serum-derived phospholipid involved in various cellular processes, including:
-Cell proliferation
-Chemotaxis
-Platelet aggregation
-Wound healing
-Angiogenesis
-Tumor invasion
-Smooth muscle contraction
Emerging research suggests LPA plays a key role in cancer pathophysiology and may serve as a biomarker for ovarian cancer.
Keywords: K-2800, K-2800B, LPA ELISA, LPA detection, Autotaxin, ATX