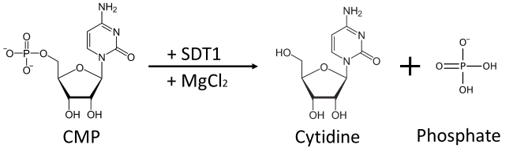
Recombinant SDT1 (Pyrimidine 5’– nucleotidase) C-terminal His-tagged fusion protein from S. cerevisiae. Purified from E.coli using Ni-NTA column chromatography. Pyrimidine 5’- nucleotidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the pyrimidine monophosphates (CMP and UMP) into their respective nucleoside and free phosphate (PO4).
Product Background:SDT1, pyrimidine 5’– nucleotidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of the pyrimidine monophosphates (CMP and UMP) into their respective nucleoside and inorganic free phosphate (PO4).[1] The enzyme is dependent on magnesium ions (Mg 2+) for activity and is susceptible to common chelating agents, such as EDTA. In addition, the enzyme demonstrates a maximum activity between pH 7.5 to 8.0.
Multiple forms of pyrimidine 5’- nucleotidases have been identified in mammals and vary by substrate specificity, distribution, cellular localization, and regulation. Dephosphorylation of nucleotides to nucleosides serves a regulatory control. For example, hereditary deficiency of pyrimidine 5’- nucleotidase is the most frequent abnormality of red blood cell nucleotide metabolism, causing a heritable form of hemolytic anemia.[2]
The SDT1 enzyme can also be used as an auxiliary enzyme in enzymatic assays to measure cytidine monophosphate (CMP) levels. The addition of SDT1 to reaction mixtures generates one free phosphate from each CMP molecule. Free phosphate levels can then be measured using a malachite green reagent, demonstrated with Echelon Biosciences products: K-2000F and K-1500.
SDT1, pyrimidine 5’– nucleotidase, catalyzes the hydrolysis of the pyrimidine monophosphates (CMP and UMP) into their respective nucleoside and inorganic free phosphate (PO4).[1] The enzyme is dependent on magnesium ions (Mg 2+) for activity and is susceptible to common chelating agents, such as EDTA. In addition, the enzyme demonstrates a maximum activity between pH 7.5 to 8.0.
Multiple forms of pyrimidine 5’- nucleotidases have been identified in mammals and vary by substrate specificity, distribution, cellular localization, and regulation. Dephosphorylation of nucleotides to nucleosides serves a regulatory control. For example, hereditary deficiency of pyrimidine 5’- nucleotidase is the most frequent abnormality of red blood cell nucleotide metabolism, causing a heritable form of hemolytic anemia.[2]
The SDT1 enzyme can also be used as an auxiliary enzyme in enzymatic assays to measure cytidine monophosphate (CMP) levels. The addition of SDT1 to reaction mixtures generates one free phosphate from each CMP molecule. Free phosphate levels can then be measured using a malachite green reagent, demonstrated with Echelon Biosciences products: K-2000F and K-1500.
Storage
Store at -20 °C. Stable for at least 6 months at -20 °C as undiluted stock
References
1) Toshiyuki Nakanishi and Kazuhisa Sekimizu,(2002); The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, No. 24, June 14, pp. 22103-22106
2) Alberto Zanella, Paola Bianchi, Elisa Fermo and Giovanna Valentini, (2006); British Journal of Haematology, 133, 113-12.