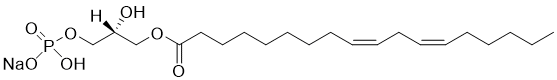
Linoleoyl LPA, 18:2 LPA is an LPA analog with an unsaturated acyl chain. Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) is a small lysophospholipid involved in diverse cellular processes such as cell proliferation, chemotaxis, platelet aggregation, wound healing, angiogenesis, tumor invasion, and smooth muscle contraction. LPA binds to several G-coupled protein receptors to initiate its biological functions. In cancer, LPA primarily promotes cell survival, migration and invasion. May contain up to 5-10% of the 2-acyl isomer due to acyl transfer.
Product Number: L-0182
Linoleoyl LPA, 18:2 LPA
Linoleoyl LPA, 18:2 LPA is an LPA analog with an unsaturated acyl chain. [Read More...]