Interleukin-17 (IL-17) is a cytokine produced by a specific type of T cell and is involved in restricting invasive microbes. Despite this positive inflammatory action, it can also cause tissue damage in autoimmune conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this light, T cell activity and IL-17 must be strictly controlled, but very little is known about these processes beyond the transcriptional level. An alternative to looking at expression patterns within these cells is examining the signaling pathways that are required for production of IL-17.
T cells have specialized T cell receptors (TCRs) that can be found in the plasma membrane. These receptors are responsible for recognizing antigen peptide fragments and are known to signal to the nucleus through some well characterized transduction pathways. However, the precise pathway for IL-17 production has not been fully described. Here, Revu and colleagues show that nuclear localization of the second messenger lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) is enhanced in TH17 T cells. This was dependent on the activity of a specific kinase, PIP5K1α, and was necessary for production of IL-17. Conversely, cytokine production in other types of T cells was not dependent on PIP5K1α activity or nuclear PIP2. In these studies, cells were stained with antibodies against the cell surface markers CD4 and CD154. Echelon's Biotinylated Anti-PtdIns(4,5)P2 IgM (Cat. #Z-B045)was used for nuclear staining.
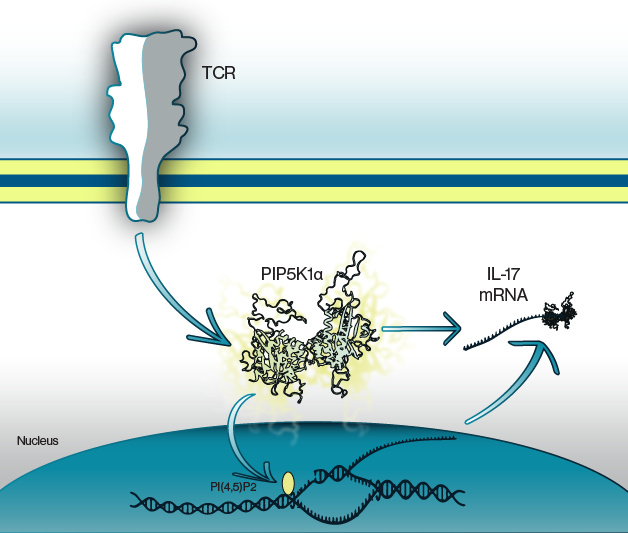
Figure 1: Activation of TCRs leads to PIP5K1α activation. This initiates production of the cytokine, IL-17, whose protein synthesis is regulated by formation of a mRNA binding complex including PIP5K1α. Likewise, inhibition of PIP5K1α blunts IL-17 production.
In MS, inflammatory T cells are autoreactive to the endogenous protein myelin basic protein (MBP) and this reactivity is partly characterized by high levels of IL-17. In the current study, T cells obtained from MS patients were activated by MBP, but downstream production of IL-17 could be blocked by inhibiting PIP5K1α. The data suggest that this occurs post-transcriptionally as PIP5K1α forms an apparent mRNA cap-binding complex to facilitate IL-17 mRNA translation. However, it remains unclear if PIP5K1α activity is required for IL-17 mRNA translation or if blockade of IL-17 production via PIP5K1α inhibitor binding is due to an allosteric action that prevents mRNA cap binding. In total, the current data highlights a new pathway for regulation of cytokine production which may hold relevance for development of therapies for autoimmune disorders.
Read the full article here:
Human IL-17A protein production is controlled through a PIP5K1α-dependent translational checkpoint
Science Signaling 16:808 (2023)
0.2
/ 0.3
Related Articles
Stay informed with our informative blog posts.
0.3
/ 0.3
Get in Touch
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about our services, feel free to reach out to us. We’re here to help!
Biosciences